 On April 2, Google stock (Nasdaq: GOOG) split into two classes of shares with two different tickers: GOOG stock and GOOGL stock. Since we still get asked "What's the difference between GOOG and GOOGL stock?," here's the answer...
On April 2, Google stock (Nasdaq: GOOG) split into two classes of shares with two different tickers: GOOG stock and GOOGL stock. Since we still get asked "What's the difference between GOOG and GOOGL stock?," here's the answer...
Companies like Google undergo stock splits to increase the number of shares outstanding while lowering share price. The move doesn't affect valuation or any other fundamentals. That's exactly what Google has done - its two-for-one split means that the company gained twice as many shares outstanding, while Google stock price lowered from $1,125 per share to about half that at $570 (on the day of the split).
Google made its intent behind increasing outstanding shares very clear. Two years ago, the tech giant announced it would make the move to increase the 56% majority control of Google co-founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin and executive chairman Eric Schmidt.
In a letter to shareholders in 2012, Page outlined the problem: stock-based employee compensation and acquisitions were undermining Google's corporate structure. Each GOOG stock the growing company gave out was having a diluting effect on upper management's majority position.
Then he proposed the stock split:
"[Management has] protected Google from outside pressures and the temptation to sacrifice future opportunities to meet short-term demands," Page wrote. "We want to ensure that our corporate structure can sustain these efforts and our desire to improve the world."
In other words, Google sees the sanctity of the upper management team as a major factor in Google's success, and wants to preserve that for the continued health of the company - and for the good of investors.
Understanding the goal of the stock split - to preserve Google's corporate structure - is the key to understanding the difference between GOOG and GOOGL stock...
The Difference Between GOOG Stock and GOOGL Stock
On April 2, investors who owned Google stock prior to the split received one share of GOOG and one share of GOOGL. GOOG stock represents Class C shares, while GOOGL stock is Class A shares. The difference is Class C shares have no voting rights, while Class A gets one vote per share.
For example, if an investor held 100 Class A shares prior to the stock split, he or she also had 100 votes. After the stock split, the same investor would have 100 Class A shares, with the same 100 votes, plus 100 Class C shares with no voting rights. That means his or her shares doubled to 200, but net voting rights remained the same.
But here's the crux of this stock split, where majority ownership really comes into play...
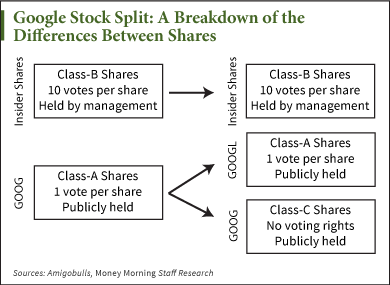 There are also Class B shares that do not trade publicly. They're owned by Page, Brin, and Schmidt, and each stock is worth a whopping 10 votes.
There are also Class B shares that do not trade publicly. They're owned by Page, Brin, and Schmidt, and each stock is worth a whopping 10 votes.
Going forward, when Google issues shares to employees for compensation, they will almost always be non-voting GOOG Class C shares. In doing so, Google will be able to offer its stock without diluting upper management's high-voting-weight Class B shares or the single-vote GOOG shares.
It also means that although new investors will be purchasing Google stock at nearly half the price, the shares they buy will have no voting power.
The Google stock split isn't the only notable one this year - Apple's seven-for-one stock split in June dropped its share price from $600 to under $100 a share. Retail investors love a "cheaper" price, and AAPL stock has benefited more than 11% after investors piled in. Here are seven other stocks with high prices that could benefit from a stock split...
Now that you know the difference between GOOG and GOOGL stock, are you buying? Join the conversation on Twitter @moneymorning using #Google.


